Breast cancer is one of the most common diseases among women and prevention, has become very important due to the limitations and high costs of treatment. A healthy lifestyle is one of the most effective factors in cancer prevention. According to studies, consumption of cruciferous vegetables, especially due to indole-3-carbinol (I3C) is associated with a reduction in the risk of breast cancer. In addition, the preventive effects of green tea extract, curcumin and vitamins D and B9 have been proven against breast cancer. For this reason, the intake of these compounds can be a natural strategy to prevent the occurrence of breast cancer in susceptible people. Since these compounds help to establish hormonal balance can be effective adjunct treatment for Human papilloma virus (HPV) infection-related diseases.
EuRho vital Indol Plus capsule contains I3C, broccoli extract, green tea extract, curcumin phospholipid complex and vitamins including vitamin D that help to prevention of cancer and treatment of HPV infection-related diseases.
Contains indole-3-carbinol, broccoli extract, curcumin phospholipid complex, green tea extract and vitamins D, C, B12 and folic acid.
- Help to prevention of breast cancer and other cancers
- Help to treatment of Human papilloma virus infection-related diseases
- Protection of cells against oxidative damage due to antioxidant properties
- Maintaining the balance of estrogen hormone in the body
| Nutrition information per 1 capsule | |
| Indole-3-carbinol | 200 mg |
| Broccoli extract | 75 mg |
| Green tea extract | 250 mg |
| Curcumin phospholipid complex | 40 mg |
| Vitamin C | 100 mg |
| Vitamin D (2000 IU) | 50 µg |
| Vitamin B12 | 10 µg |
| Folic acid | 400 µg |
Broccoli extract and I3C:
Cruciferous vegetables are rich sources of sulfur-containing compounds known as glucosinolates and relatively good sources of nutrients that may have protective effects against cancer, including vitamin C, folate, selenium, carotenoids, and fiber. I3C is one of the most important chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic glucosinolates found in cruciferous vegetables including broccoli, which decomposes into the effective compound 3,3’-diindolylmethane (DIM) after consumption. Studies show that these compounds can suppress the growth of breast cancer cells and other cancers including ovarian, prostate, endometrium and colon.
Biological Activities of I3C:
- Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) pathway: I3C and DIM regulate the expression of phase 1 detoxification enzymes via the AhR signaling pathway. Increasing the activity of biotransformation enzymes is generally considered a beneficial effect because the elimination of potential carcinogens or toxins is enhanced.
- Nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) -dependent pathway: I3C and DIM have been shown to induce the expression of phase II detoxifying and antioxidant enzymes via the activation of the Nrf2-dependent pathway.
Modulation of cell-signaling pathways of I3C:
- Cell cycle arrest: Inhibition of CDK6 expression and activity and reduction of CDK2 activity, two G1-acting CDKs, by I3C in breast cancer cells are responsible for the decrease in retinoblastoma protein (Rb) phosphorylation and thereby cell cycle arrest.
Furthermore, in human ovarian cancer cells, DIM has been shown to suppress cell growth and division through activating G2/M arrest via the checkpoint kinase 2-dependent pathway.
- Angiogenesis: I3C inhibit the LPS-induced formation of capillary-like structures by endothelial cells, decreasing secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), nitric oxide (NO), IL-6, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and inhibits angiogenesis.
- Metastasis: In estrogen-responsive breast cancer cells, I3C treatment resulted in significant inhibition of in vitro cell adhesion, migration, and invasion.
- Apoptosis: I3C has been found to induce apoptosis by upregulating or downregulating apoptosis markers/proteins in key pathways. I3C appears to induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells, but not in non-cancer cells.
Estrogen metabolite ratio:
The ratio of 2-hydroxyestrone /16-α-hydroxyestrone is a biomarker for risk of estrogen-dependent cancer and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). I3C increases the production of the antiproliferative metabolite 2-hydroxyestrone and decreases the production of 16-α-hydroxyestrone as a human carcinogen.
Regulation of inflammation:
DIM inhibited TPA-induced activation of kinases (inhibitor of kappa B kinase [IκK] and extracellular signal-regulated kinase [ERK]) that control the transcriptional activity of NF-κB, a major transcription factor regulating the expression of many pro-inflammatory genes.
Disease Prevention and treatment:
As mentioned, cruciferous vegetables and their effective ingredients especially I3C effective in preventing cancer. In addition, these compounds also help to treatment of HPV infection-related diseases.
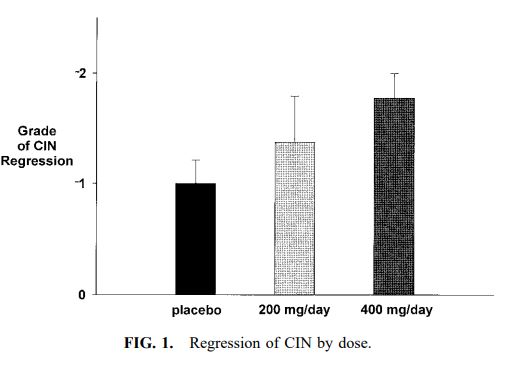
- Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN): I3C doses of 200 or 400 mg/day improved the regression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia.
- Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN): A randomized trial in women with VIN found that supplementation with 200 or 400 mg/day of I3C for six months improved overall symptoms, as well as lesion size and appearance.
- Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: I3C may be an effective adjunct treatment to reduce the growth or recurrence of respiratory papillomatosis.
Green tea extract: Down-regulate oncogenes and up-regulate tumor-suppressor genes and exerts protective effects against tumorigenesis owing to its principal polyphenol, namely epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). EGCG can induce programmed cell death in breast cancer cells and modulate multiple cells signaling pathways implicated in angiogenesis, metastasis and invasion.
Curcumin: Curcumin influences on cell cycle and proliferation, natural cell death, cancer spread and development of new blood supply to support tumor progression. The key signaling pathways involved include the NFkB, PI3K/Akt/mTOR, MAPK and JAK/STAT. The chemopreventive effects of curcumin towards mammary tumorigenesis has been observed in both the initiation and post-initiation phases.
The curcumin in this product is in the form of microencapsulated curcumin that has better bioavailability, absorption and superior antioxidant property, than free curcumin.
Vitamin D: This vitamin inhibits the growth of cells by inhibiting the proliferation process. Also, vitamin D stimulates the death of cancer cells due to its pro-apoptotic properties. The results of studies have shown the preventive effects of vitamin D against breast cancer.
Folic acid: Reduce risk of breast, ovarian, and uterine cancer.
Vitamin C: It has antioxidant properties.
Vitamin B12: Participates in cell division.
